Blog / Ultimate Guide to Scalable Workflow Automation Frameworks
Ultimate Guide to Scalable Workflow Automation Frameworks
Workflow automation frameworks streamline repetitive tasks using predefined rules and triggers. They save time, reduce errors, and improve efficiency. For businesses in the UAE, scalability in these systems is critical to handle growing demands without disruptions. Key highlights include:
- Scalability: Ensures systems can manage increased workloads without performance issues.
- Benefits: Saves time (up to 3.5 hours/week), boosts productivity (up to 80%), and improves accuracy by 90%.
- Approaches: Horizontal scaling (adding machines), vertical scaling (upgrading resources), and microservices for independent scaling.
- Challenges: State management, bottlenecks, and infrastructure costs.
- Solutions: Modular design, real-time data integration, and hybrid workflows.
Scalable frameworks are essential for UAE businesses in fast-paced sectors like e-commerce and logistics to stay efficient and competitive.
The Ultimate Guide to Building Production-Ready n8n Workflows
Core Principles of Scalability in Workflow Automation
Horizontal vs Vertical Scaling in Workflow Automation: Key Differences
Creating scalable workflow automation systems relies on understanding three key principles that support growth. These principles form the backbone of the design patterns and architectures discussed in the following sections.
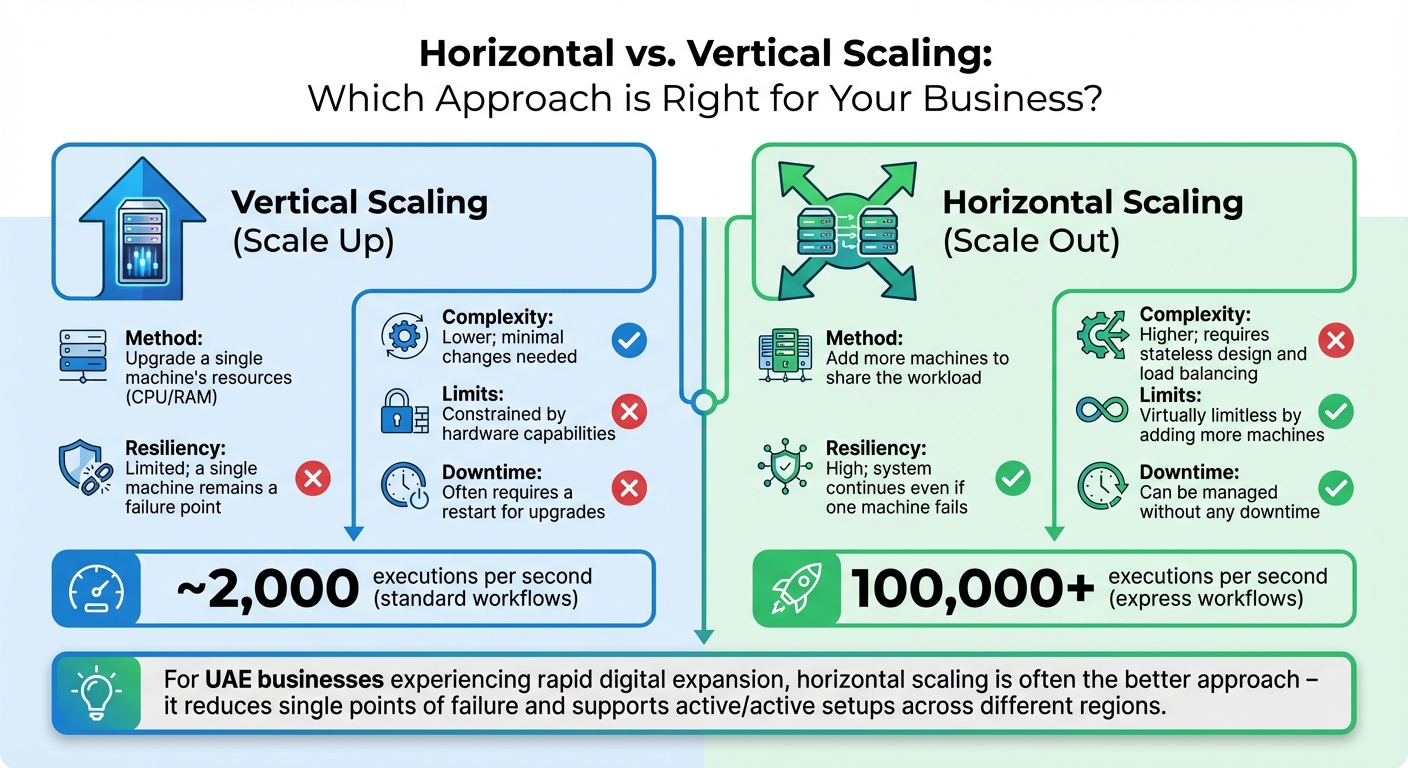
Horizontal vs. Vertical Scaling
Vertical scaling (or scaling up) involves upgrading the resources of a single server - whether that’s adding more CPU power, RAM, or storage. This method is often suitable for workloads that aren’t easily split across multiple systems or when your setup doesn’t support distributed processing. However, it has its limitations; at some point, you’ll hit the maximum capacity of the hardware.
Horizontal scaling (or scaling out), on the other hand, adds more servers or containers to share the workload across multiple machines. For businesses in the UAE experiencing rapid digital expansion, this is often the better approach. It reduces single points of failure and supports active/active setups, where the workload is spread across different regions or zones. The trade-off? It’s more complex. Your system needs to function seamlessly across multiple machines without depending on any single one.
To put this into perspective, standard workflows handle approximately 2,000 executions per second, while high-volume express workflows can process over 100,000 executions per second.
| Feature | Vertical Scaling (Scale Up) | Horizontal Scaling (Scale Out) |
|---|---|---|
| Method | Upgrade a single machine's resources (CPU/RAM) | Add more machines to share the workload |
| Complexity | Lower; minimal changes needed | Higher; requires stateless design and load balancing |
| Resiliency | Limited; a single machine remains a failure point | High; system continues even if one machine fails |
| Limits | Constrained by hardware capabilities | Virtually limitless by adding more machines |
| Downtime | Often requires a restart for upgrades | Can be managed without any downtime |
Next, we’ll delve into how decoupled systems and microservices support scalability.
Decoupled Systems and Microservices
A decoupled architecture breaks workflows into separate components that communicate through defined interfaces. Instead of relying on one large system, you create smaller, independent services tailored to specific tasks. This allows each component to scale independently based on its needs rather than scaling the entire system as a whole.
One of the biggest advantages of this approach is fault isolation. For example, if a payment gateway service fails, other parts of the system - like inventory management or customer notifications - can keep running without disruption. As Programming Pulse puts it:
High cohesion in microservices is akin to kitchen organisation - it means that each microservice is laser-focused on a specific task or functionality.
A critical part of this setup is statelessness. When services don’t retain client-specific data between requests, any instance can handle incoming requests, making horizontal scaling much easier. Businesses should also follow the Single Responsibility Principle, ensuring each microservice focuses on a single function to avoid creating a system that’s essentially a monolith in disguise. Using orchestrators can help keep routing logic clean and prevent it from becoming tangled in individual functions.
Load Balancing and Fault Tolerance
Fault tolerance ensures that your system can keep running - even if parts of it fail - while load balancing spreads requests across resources to handle traffic surges without bottlenecks. Together, these strategies are essential for resilient automation.
Queue-based load levelling is a common technique where message queues temporarily store requests during peak times. This keeps the user interface responsive while background processes catch up during quieter moments. For long-running tasks, saving the process state at regular intervals allows the system to recover from the last saved point instead of starting over. The Bulkhead pattern is another useful strategy, dividing service instances into groups to ensure that a failure in one doesn’t disrupt the entire system.
Adding dead letter queues is also crucial. These error-handling buffers capture problematic messages that repeatedly fail, preventing them from clogging the entire workflow. To manage costs during unexpected traffic spikes, businesses can set limits on autoscaling units. And when autoscaling isn’t enough to handle sudden demand, a throttling pattern can protect the system by intentionally slowing down the processing rate.
For UAE businesses, targeting low-latency zones (less than 2 ms) is key for seamless inter-zone performance. As Scalevise explains:
Scalability is not just about running the same workflow for more users. It is the ability to increase volume, complexity or frequency without degrading performance or creating chaos in your systems.
Key Architectures for Scalable Workflow Automation
When it comes to building scalable workflow automation systems, selecting the right architecture is crucial. Among the leading options are event-driven workflow engines, container-native platforms, and serverless workflow orchestrators. Each approach caters to different business needs, technical capabilities, and workload patterns. Let’s dive into how these architectures meet specific scalability challenges.
Event-Driven Workflow Engines
Event-driven architectures excel at managing workflows triggered by specific events, making them perfect for businesses that face unpredictable or fluctuating workloads. For example, platforms like Cadence rely on a stateless backend combined with a persistent, sharded datastore (e.g., Cassandra or MySQL). This setup provides "durable virtual memory", preserving the entire application state - including function stacks and local variables - even during host or software failures.
One major advantage is asynchronous processing. These systems trigger downstream events that execute independently, avoiding I/O bottlenecks. By doing so, they can manage complex, long-running distributed applications without tying up resources. For UAE businesses handling high-frequency transactions or IoT data streams, this architecture ensures workflows remain uninterrupted, even when individual components face issues. This dynamic approach perfectly aligns with the scalability principles discussed earlier, as it adapts to unpredictable workloads with ease.
Container-Native Platforms
Container-native platforms, such as Argo Workflows, Flyte, and Kubeflow Pipelines, are built on Kubernetes and are widely recognised for their ability to orchestrate parallel jobs at scale. Each workflow step is executed in its own container, enabling efficient parallel processing for resource-intensive tasks like training machine learning models or processing large datasets.
The standout feature here is portability. Since workflows are containerised, they can be deployed consistently across different environments - whether on-premises, in the cloud, or in hybrid setups. This flexibility is especially useful for businesses that need to maintain control over their infrastructure while ensuring smooth and predictable performance across varying conditions.
Serverless Workflow Orchestrators
Serverless workflow orchestrators, such as AWS Step Functions and Google Cloud Workflows, take a different approach by removing the need to manage infrastructure. These systems automatically scale from a handful of executions to millions, making them ideal for both long-running and high-speed workflows.
A real-world example from 2023 is CyberGRX, which used AWS Step Functions’ Distributed Map feature to process large-scale security logs and transaction data. This significantly reduced the time required for machine learning tasks.
To better understand the differences between serverless orchestrators and container-native platforms, here’s a quick comparison:
| Feature | Serverless Orchestrators | Container-Native Platforms |
|---|---|---|
| Infrastructure | Fully managed; no need to provision servers | Requires managing container clusters (e.g., Kubernetes) |
| Scaling | Automatic, on-demand scaling from zero to millions of executions | Scaling depends on container orchestration and node availability |
| Development | Often low-code/visual, using JSON or YAML | Developer-intensive; requires containerisation and code-based definitions |
| Cost Model | Pay-per-use based on execution time or transitions | Typically involves fixed costs for maintaining clusters and nodes |
| Integration | Deep native integration with cloud ecosystems | Portable across environments but requires manual integration setup |
For UAE businesses prioritising cost efficiency and ease of operations, serverless orchestrators are a great fit. For instance, AWS Step Functions offers a free tier with 4,000 state transitions per month, making it a budget-friendly option for smaller-scale needs.
These architectural frameworks provide the foundation for creating scalable and efficient automation systems, paving the way for exploring advanced design patterns in the next section.
Design Patterns for Scalable Workflow Frameworks
After understanding the architectural foundations, let’s explore design patterns that help create workflows that scale effectively. These patterns focus on modularity, real-time data usage, and combining different architectural styles to improve efficiency and scalability.
Modular and Reusable Components
Breaking workflows into smaller, single-purpose components makes them easier to test, reuse, and maintain. This approach also reduces the risk of system-wide failures.
For instance, instead of duplicating customer data validation logic across multiple workflows, you can create a reusable subworkflow for validation. This simplifies updates and supports horizontal scaling - once a workflow is stable, it can be reused across other processes without adding unnecessary complexity.
To ensure smooth operation, design stateless functions that initialise state at the start, commit changes to durable storage, and track processed IDs for idempotency. Use tools like environment variables or secret managers to keep configurations flexible, allowing components to work seamlessly across staging and production environments.
For workflows involving multiple microservices, the Saga pattern can help manage data consistency. It ensures that a series of transactions are completed in sequence, with compensating actions triggered automatically in case of failures.
The next step is leveraging real-time data to make workflows more adaptive and efficient.
Data-Driven Automation
Real-time data insights play a key role in making workflows scalable and adaptive. By validating data schemas between workflow stages, you can maintain data integrity and avoid issues like "prompt drift" in AI workflows.
In high-volume scenarios, optimising data formats can save costs. For example, the TOON format compresses complex JSON into a token-based structure, reducing API token usage in AI workflows. This is especially relevant given OpenAI's rapid growth, with over US$1 billion in annual recurring revenue added in just one month as businesses integrate AI into their systems.
To handle traffic spikes, integrate queues (like Amazon SQS) or streams (such as Kinesis) as a buffering layer between APIs and backends. This ensures durability and smooth processing during high-traffic periods. For processing large datasets, use parallel steps or Map states to handle files (e.g., CSVs or logs stored in S3) concurrently, speeding up execution. Additionally, static initialisation in functions can maintain database connections across multiple invocations, improving performance as the system scales.
With data insights in place, adopting a hybrid approach can further optimise scalability.
Hybrid Approach for Optimised Scalability
A hybrid approach combines the simplicity of direct service-to-service communication with the flexibility of event-driven orchestration. This balance often offers the best performance for complex workflows.
Tiered workflow execution is one strategy to consider. For example, AWS Step Functions’ Express Workflows are ideal for short, high-volume tasks, while Standard Workflows handle long-running processes. Express Workflows can process over 100,000 executions per second, compared to around 2,000 per second for Standard Workflows. Matching the workflow type to the workload helps optimise both performance and cost.
Event-driven orchestration is another key element. It allows related services to work together without being tightly coupled. You can also mix serverless functions for lightweight tasks with containerised jobs (using tools like Cloud Run or Batch) for more resource-intensive operations.
For workflows requiring human oversight, include human-in-the-loop steps. These steps allow scalable automation while enabling manual approvals for critical decisions. Additionally, modern systems increasingly use LLM-powered "Agentic AI" for tasks requiring non-linear reasoning that traditional code struggles to handle. With the cost of querying GPT-3.5-level AI dropping significantly between 2022 and 2024, these AI-driven solutions are now cost-effective for high-volume use cases.
| Pattern | Recommended Service/Tool | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Queue | Amazon SQS | Handles traffic bursts with buffering |
| Orchestration | AWS Step Functions | Manages complex branching and retries |
| Event Bus | Amazon EventBridge | Decouples services through event triggers |
| State Tracking | Amazon DynamoDB | Tracks processed IDs for idempotency |
| Data Transformation | AWS Lambda | Processes data in parallel for efficiency |
sbb-itb-058f46d
Common Scalability Challenges and Solutions
Scalability Challenges Across Platforms
Scalable workflow automation frameworks often face a range of technical hurdles. One major issue is state management, which becomes tricky when workflows access shared datasets simultaneously. For instance, processes that work well in staging environments often fail in production due to conflicts with shared datasets. Another challenge is throughput bottlenecks, where sequential execution delays updates like security patches and product releases.
Fault tolerance is another common pain point. Unpredictable test outcomes - caused by unhandled asynchronous operations, network instability, or fragile locators - can disrupt workflows. Then there’s the issue of infrastructure scaling. Maintaining in-house servers for high-volume execution is not only expensive but also risky. Without proper auto-scaling configurations, servers can crash during sudden traffic spikes. The maintenance trap adds to these problems: as applications evolve, changes in UI or APIs often break existing automation scripts. This forces teams to spend more time fixing scripts rather than developing new ones.
Early warning signs of scalability issues include repeated manual inputs across tools, rising API costs that outpace business growth, developers repeatedly rerunning inconsistent tests, and critical process logic being siloed within specific team members' knowledge. Alarmingly, only 24% of organisations have managed to automate at least half of their test cases, indicating a significant gap in scalability.
The table below highlights the differences between scalable and non-scalable frameworks:
| Attribute | Scalable Framework | Non-Scalable Framework |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture | Modular, component-driven | Monolithic, poorly structured |
| Data Handling | Separated from logic | Hardcoded within scripts |
| Environment | Independent, containerised | Tied to specific local setups |
| Execution | Parallel and distributed | Sequential and slow |
| Maintenance | Self-healing, low effort | Brittle, high manual effort |
Different platforms tackle these challenges in unique ways. Camunda (Zeebe) uses event-streaming to persist state outside a central database, avoiding input/output bottlenecks. Cadence employs event sourcing, allowing workflows to recover state through event history replay, making them resilient to worker or service downtime. Temporal relies on durable execution to recreate pre-failure states from event history, although its scalability can be limited by shard configurations set during build time.
A real-world example comes from Martin Schneider, Delivery Manager, who shared how switching to BrowserStack's cloud-based automated testing reduced his team's testing time from a full day (involving eight engineers) to just one hour, enabling the possibility of daily releases.
Understanding these challenges is the first step toward building targeted solutions.
Solutions for Optimising Scalability
Addressing scalability issues requires a mix of strategic and technical solutions. Start by implementing observability to monitor system performance. Track key metrics like request rates, latency, database errors, and workflow execution statistics (success and failure rates) to predict when systems are nearing their limits.
Modular design patterns are essential. By separating test logic from data and page interactions - using frameworks like the Page Object Model - you can ensure that a single UI update doesn’t require rewriting the entire automation suite. For workflows involving AI, optimise API costs by adopting compact data formats like TOON, which reduce token consumption. This approach is especially relevant as OpenAI's API business continues to grow rapidly, adding over US$1 billion in annual recurring revenue in a single month.
Parallel execution is another key strategy. Shift from sequential processing to concurrent execution across multiple threads or cloud environments to maintain throughput. Caching task outputs can further reduce redundant computations and save resources. For large-scale problems, use child workflows to break tasks into smaller, manageable pieces. For instance, a parent workflow can oversee 1,000 child workflows, each handling 1,000 activities - scaling up to 1 million activities without exceeding history size limits.
"Before BrowserStack, it took eight test engineers a whole day to test. Now it takes an hour. We can release daily if we wanted to." - Martin Schneider, Delivery Manager
To manage costs, consider using spot or interruptible instances for non-critical tasks, which can significantly lower cloud expenses. Over-provision resources to run at 75% utilisation, leaving enough capacity to handle sudden spikes in traffic, as scaling operations can take up to 45 minutes to stabilise. Finally, integrating AI-driven self-healing automation can drastically cut down maintenance time - by as much as 99.5%, according to organisations using platforms like testRigor.
Wick's Four Pillar Framework for Marketing Workflow Optimisation

As businesses in the UAE embrace advanced technology at an unprecedented pace, the Intelligent Process Automation market is expected to hit AED 9.2 billion (approximately $2.5 billion) by 2030, with an annual growth rate of 20%. This growth aligns with the UAE government's push for a smart, digitally-driven economy. In this landscape, Wick's Four Pillar Framework offers a streamlined approach to integrating technical efficiency with marketing strategies. By combining website development, SEO, content creation, marketing automation, and AI-driven personalisation, Wick creates a unified digital ecosystem designed for scalable growth. These pillars work together to transform complex marketing workflows into actionable, efficient strategies.
Build & Fill: Laying the Foundation for Growth
The Build & Fill pillar focuses on setting up the core infrastructure needed for efficient marketing operations. For instance, automated SEO reporting connects directly to tools like Google Analytics and SEMrush through APIs, cutting reporting time from hours to mere minutes. This automation also extends to content creation workflows, freeing up marketing teams to focus on strategic initiatives. By establishing this robust foundation, businesses are better positioned to leverage the advanced personalisation capabilities introduced in the next phase.
Tailor & Automate: Scaling with AI Precision
The Tailor & Automate pillar harnesses AI to optimise marketing workflows without requiring significant increases in workforce size. Wick's AI systems are trained on each business's specific data, terminology, and operational rules, enabling them to handle repetitive tasks like data entry and report generation with exceptional accuracy.
For example, a trading company in Dubai handling over 300 daily orders integrated AI into its existing ERP system. This reduced order processing time from 45 minutes to just 11 minutes - an impressive 75% improvement. Errors dropped from 8% to a negligible 0.1%, and the company achieved full ROI in only four months. By combining AI-driven automation with human oversight, teams can increase their capacity tenfold. AI takes care of initial tasks like research and drafting, while human experts focus on strategic and creative elements. This approach ensures a seamless blend of efficiency and personalisation, paving the way for system-wide integration.
Long-Term Growth Through System Integration
Wick's framework goes beyond isolated solutions by seamlessly integrating with widely used platforms such as Salesforce, HubSpot, Zoho, SAP, Oracle, and Microsoft Dynamics. Custom middleware ensures smooth coordination across these systems, allowing AI to track decisions and enabling human intervention when necessary.
In one notable example, a manufacturing firm in Riyadh used AI to automate procurement and inventory workflows. By analysing five years of historical data, the company reduced approval cycles from seven days to just four hours, saving AED 7.7 million (around $2.1 million) annually in operational costs. With bilingual Arabic-English support, Wick ensures smooth communication within the GCC region. Additionally, its compliance features align with the UAE Data Protection Law and GDPR requirements, offering businesses peace of mind.
Conclusion
Best Practices for Scalability
Creating scalable workflow automation frameworks starts with treating them like solid software infrastructure. This means prioritising clear documentation, version control, and ongoing monitoring to prevent fragile systems that are prone to breaking down. A modular design is key here - breaking processes into manageable components, such as lead intake, qualification, and routing. This approach allows for targeted scaling without overcomplicating the system.
"Scalable workflow automation is no longer a luxury. It is a requirement for any organisation that wants to operate efficiently, reduce operational risk and stay competitive in a market where speed and accuracy define growth." - Scalevise
Governance should be built into the framework from the very beginning. This includes establishing access controls, ensuring auditability, and setting clear protocols for managing sensitive data - especially important in regulated industries like finance and healthcare. Scalable infrastructure that can adapt to fluctuating demand is another critical piece of the puzzle. Additionally, adopting observability-focused platforms helps track key metrics such as volume, latency, and failure trends.
By following these practices, organisations can ensure their systems remain reliable and high-performing over the long term. These principles serve as the backbone of the strategies discussed throughout this guide and provide a strong starting point for tailored, integrated solutions like those offered by Wick.
Wick's Role in Supporting Scalable Solutions
Wick takes these best practices and integrates them into marketing operations with precision. Its Four Pillar Framework, outlined earlier, is specifically designed to address the unique challenges faced by UAE businesses when scaling their marketing efforts. By combining website development, SEO, content creation, and AI-driven personalisation into a single, cohesive ecosystem, Wick eliminates the common issue of data silos that often disrupt workflows.
The framework also includes custom middleware that ensures AI decisions are logged, data exchanges are tracked, and human intervention remains an option when necessary. This thoughtful blend of technical infrastructure and regulatory compliance enables UAE businesses to scale their operations efficiently while maintaining strong governance.
Wick’s approach transforms fragmented marketing tools into a unified, scalable system, positioning enterprises for long-term growth in a competitive market.
FAQs
What are the advantages of scalable workflow automation frameworks for businesses in the UAE?
Scalable workflow automation frameworks offer UAE businesses a practical way to boost efficiency, improve accuracy, and expand operations without inflating costs. By automating repetitive tasks - like email marketing, lead qualification, and order processing - these systems save valuable time while cutting down on human errors. This is particularly crucial in the UAE, where the market moves quickly and operates within a multicultural environment.
These frameworks also work effortlessly with tools such as CRM and ERP platforms, ensuring a seamless flow of data and enabling real-time decision-making. For companies in the UAE, automation solutions address specific local requirements, including compliance with regulations, the need for bilingual content, and cultural considerations like Ramadan schedules. By embracing these systems, UAE businesses can position themselves for steady growth and maintain a competitive edge on a global scale.
What is the difference between horizontal and vertical scaling in workflow automation?
In the realm of workflow automation, horizontal scaling and vertical scaling are two common strategies for boosting a system's capacity, each catering to different needs.
With horizontal scaling, you expand the system by adding more machines or nodes. This distributes tasks across multiple units, making it well-suited for workloads that demand flexibility and the ability to handle broad distribution. Think of it as spreading the load across a team rather than relying on a single individual.
In contrast, vertical scaling upgrades the resources of a single machine - like increasing its CPU, RAM, or storage. This approach is ideal for systems that need more power but operate in a centralised, stable environment, avoiding the complexity of managing multiple units.
The choice between these two strategies hinges on your specific requirements. If your system handles large, distributed workloads, horizontal scaling is the way to go. For systems that prioritise performance in a centralised setup, vertical scaling is the better option.
How can businesses build fault-tolerant workflow automation systems?
To create workflow automation systems that can withstand failures, businesses need to focus on designing processes capable of identifying and resolving issues on their own. This involves integrating self-healing mechanisms that can manage minor problems without requiring manual effort, keeping operations running smoothly.
Some effective approaches include employing durable state management to preserve data integrity, implementing retry logic with exponential backoff to handle temporary failures, and designing systems to manage failed tasks in a controlled way. Moreover, using observability tools allows real-time monitoring of workflows, making it easier to spot and address potential problems quickly.
By blending resilient design principles, automated recovery methods, and comprehensive monitoring, businesses can keep their workflows dependable and available, even when unexpected challenges arise.
