Blog / 7 Machine Learning Models for Audience Segmentation
7 Machine Learning Models for Audience Segmentation
Audience segmentation is key to delivering tailored marketing in a diverse region like the UAE, where customer groups vary widely - Emiratis, expatriates, tourists, and high-net-worth individuals. Traditional methods often fall short in identifying deeper patterns within customer data. Machine learning (ML) models offer a faster, more precise way to segment audiences using behavioural and transactional data.
Here’s a quick overview of seven ML models for audience segmentation:
- K-means Clustering: Groups customers based on shared traits; works well with large datasets but struggles with irregular clusters.
- Hierarchical Clustering: Builds nested audience segments; ideal for smaller datasets but less scalable.
- DBSCAN: Focuses on data density, handling noisy or irregular datasets effectively.
- Decision Trees: Rule-based segmentation; simple, transparent, and efficient for structured data.
- Random Forests: Combines multiple decision trees for higher accuracy, especially with complex datasets.
- Neural Networks: Analyses high-dimensional data to identify patterns but requires significant computational resources.
- PCA (Principal Component Analysis): Reduces data complexity, improving the speed and accuracy of other models.
Each model has strengths and limitations, so the best choice depends on your dataset, segmentation goals, and available resources. For UAE businesses, ML-driven segmentation can lead to higher ROI, better customer targeting, and real-time adaptability in marketing strategies.
Machine Learning Models for Audience Segmentation: Performance Comparison
How to Build Customer Segments with AI (Real-World Use Case)
1. K-means Clustering
K-means clustering is a straightforward yet powerful method for grouping large customer datasets by using centroid-based partitioning techniques. Essentially, the algorithm identifies centroids that represent the core traits of each segment. For example, when analysing a dataset of 500,000 customers based on metrics like purchase frequency, average spend, and last interaction date, K-means can sort them into distinct groups in just minutes. Let’s dive into how K-means handles large-scale datasets efficiently.
Scalability for Large Datasets
K-means is highly effective when working with large customer databases. In 2023, Foursquare’s engineering team applied K-means to a dataset of around 100,000 users from their U.S. mobile location panel, using 16 features such as store visit frequency, dwell time, and income. By combining Principal Component Analysis (PCA) to reduce dimensionality with K-means, they identified six unique holiday shopping segments, enabling advertisers to target specific audience profiles. Thanks to its linear time complexity, K-means can process thousands - or even millions - of data points using standard machine learning libraries.
Suitability for Noisy or Complex Data
While K-means is fast and effective, it does have limitations, particularly with outliers and irregularly shaped clusters. The algorithm assumes clusters are spherical and of similar size, which doesn’t always align with real-world customer patterns. To overcome this, H&M in 2022 paired K-means with Gaussian Mixture Models (GMM) to analyse transactional and app clickstream data. This hybrid approach uncovered nine distinct buyer types, leading to a 70% increase in click-through rates and tripling conversions from targeted app offers.
Interpretability of Results
One of the standout features of K-means is how easy it is to interpret its results. Each cluster is defined by a centroid, which represents the average characteristics of its members. Sean Hughes, Designer at Fulcrum Analytics, highlights this advantage:
"K-Means Clustering is a reasonable starting point for most forms of customer segmentation projects. It is easy to implement, can scale to large datasets, and can be applied directly to new data points".
In one study involving 1,414 customers, K-means identified four distinct groups - Champion, Loyalist, Potential, and At Risk - using the Elbow Method to determine the optimal number of clusters. This clarity makes it simple to explain the results to stakeholders and implement targeted marketing strategies. Beyond its transparency, K-means also delivers exceptional speed, which we’ll explore next.
Computational Efficiency
K-means is designed to converge quickly by iteratively minimising the within-cluster sum of squares (WCSS) until the assignments of data points stabilise. However, proper data preparation is crucial for achieving optimal results. It’s important to normalise the data beforehand, use methods like the Elbow Method or Silhouette Coefficient to determine the ideal number of clusters, and run multiple initialisations to avoid suboptimal outcomes. For high-dimensional datasets, applying PCA to reduce the number of features - while retaining over 80% of the explained variance - can significantly enhance clustering efficiency.
This combination of speed, clarity, and adaptability makes K-means a solid foundation for exploring more advanced models capable of handling complex data in future sections.
2. Hierarchical Clustering
Hierarchical clustering takes a different approach from K-means by building a tree-like structure that captures nested audience segments. Unlike K-means, it doesn’t require you to decide the number of clusters in advance. Instead, it creates a full hierarchy, starting with individual data points and merging them into a single group, giving you flexibility to choose the best segmentation level.
Interpretability of Results
One of the key advantages of hierarchical clustering is the dendrogram - a visual representation that shows how clusters merge at each stage. This tool is particularly useful for uncovering nested relationships, making it ideal for tasks like tissue classification or document clustering. While the dendrogram is excellent for visualising how clusters relate to one another, pinpointing the optimal number of clusters from it can be tricky.
To get the most out of the dendrogram, avoid relying solely on automated methods like cutting at the longest vertical line. Instead, combine the visual insights with your domain expertise to make informed decisions about segment validation.
Scalability for Large Datasets
One drawback of hierarchical clustering is its difficulty with scaling. It requires the creation of a proximity matrix with a size of n × n, where n represents the number of data points. This makes it impractical for datasets exceeding 10,000 rows. As a result, this method is better suited for smaller datasets where understanding the complete relationship structure is more important than speed.
Suitability for Noisy or Complex Data
Unlike K-means, which assumes clusters are spherical, hierarchical clustering can handle clusters of varying shapes and sizes. However, it’s not as effective at dealing with noisy data compared to density-based methods. To improve accuracy, ensure you normalise numerical features beforehand, as this algorithm relies on Euclidean distance. For datasets with substantial noise, you might want to explore density-based techniques, which focus on grouping points by density rather than distance from centroids.
This exploration of hierarchical clustering naturally leads to density-based methods, which address some of its limitations.
3. DBSCAN
DBSCAN, which stands for Density-Based Spatial Clustering of Applications with Noise, takes a different approach to clustering by focusing on the density of data points. Instead of assuming that clusters are neat, circular shapes, DBSCAN identifies dense regions of data points separated by less dense areas. This flexibility makes it ideal for analysing complex datasets, such as behavioural patterns in clickstream data, where customer groups rarely form tidy clusters. Its ability to handle irregular shapes and filter out noise makes it particularly effective for tackling real-world challenges.
Suitability for Noisy or Complex Data
One of DBSCAN's standout features is its ability to manage outliers effectively. It categorises points into three types: core, border, and noise. This classification ensures that data points falling below the density threshold are excluded, which helps differentiate between central customers in a segment and those on the edges. This precision is invaluable for targeted marketing.
For example, in 2023, Alibaba's DAMO Academy applied DBSCAN to segment B2B merchants based on buyer behaviour density. By identifying irregular purchasing patterns, they achieved an 18% increase in reactivating previously inactive sellers. Similarly, Booking.com combined DBSCAN with sequence-based algorithms to classify traveller behaviours. They discovered that travellers booking airport taxis were 42% more likely to purchase insurance. By displaying insurance options before the taxi checkout, Booking.com saw an 11.5% boost in cross-sell revenue and reduced checkout bounce rates by 17%.
Computational Efficiency
While DBSCAN offers advanced clustering capabilities, it is memory-intensive and requires more computational resources compared to simpler models like K-means. Additionally, it cannot directly classify new data points, necessitating the use of a separate classifier. Determining the optimal "epsilon" (eps) value - critical for defining cluster density - often involves using a k-nearest neighbours (k-NN) distance plot to find the "elbow" or jump point in the curve. Preprocessing steps like feature scaling (e.g., Z-score standardisation) are essential since the algorithm relies on distance metrics to evaluate density.
Interpretability of Results
Unlike K-means, DBSCAN eliminates the need to predefine the number of clusters. Instead, it identifies natural groupings based on data density. Netflix provides a great example of this in action. By integrating DBSCAN into a machine learning pipeline with customised neural embeddings, they segmented users based on shifts in viewing preferences and watch-time velocity. This approach led to a 17% improvement in post-release engagement and a 35% reduction in trailer skips within the first five minutes.
4. Decision Trees
Decision trees offer a straightforward, rule-based method for audience segmentation, making them a transparent alternative to density-based models. Using a branching structure, decision trees split audiences into distinct segments based on customer attributes and behaviours. Unlike clustering models that group similar data points, decision trees follow a step-by-step hierarchy, clearly outlining each segmentation decision along the way. This clarity is especially useful when presenting segmentation insights to stakeholders or marketing teams who may not have technical expertise. Let’s dive into their strengths in terms of interpretability, scalability, and efficiency.
Interpretability of Results
One of the most appealing aspects of decision trees is their transparency. Unlike "black box" models such as neural networks, decision trees rely on clear, rule-based logic. Each branch represents a specific decision - such as classifying customers by spending habits or engagement levels. This makes them easy to understand, even for non-technical audiences. They operate much like traditional manual segmentation but go further by identifying micro-segments that human analysts might miss.
Scalability for Large Datasets
Decision trees shine when it comes to handling large datasets. Whether you’re segmenting 10,000 customers or scaling up to 1 million, decision trees adapt seamlessly to the increased data volume while uncovering intricate patterns across various features. This scalability is especially valuable in fast-growing markets like the UAE, where businesses often deal with rapidly expanding customer bases.
Computational Efficiency
Another advantage is their efficiency. Decision trees require far less computing power compared to deep learning models while still producing reliable segmentation outcomes. This makes them a great option for organisations with limited resources or those prioritising simplicity and transparency over complexity. Additionally, decision trees are particularly effective with structured, categorical, and behavioural data - such as information collected from CRM systems, website analytics, or transaction records.
sbb-itb-058f46d
5. Random Forests
Random forests bring together multiple decision trees to create a powerful ensemble model. This method enhances both accuracy and dependability, especially when working with noisy or intricate audience data. Instead of depending on a single decision path, random forests merge predictions from many trees - sometimes dozens or even hundreds - minimising the risk of overfitting.
Suitability for Noisy or Complex Data
Random forests are particularly effective when dealing with complex datasets, a common challenge in marketing analytics. The model evaluates a wide range of signals, such as visit frequency, category preferences, and content consumption patterns, to understand how these variables interact rather than focusing on just a few obvious traits. It can also uncover subtle correlations that might escape human analysts, like specific behavioural patterns that consistently lead to higher conversion rates.
Scalability for Large Datasets
One of the standout features of random forests is their ability to scale effortlessly, whether you're analysing data for 10,000 customers or 1,000,000. This makes them an excellent fit for businesses in the UAE's fast-growing digital economy. The best part? Scaling up doesn’t require a complete overhaul of the model or infrastructure. The same setup can handle larger datasets while maintaining accuracy and performance. For instance, at Wick, random forests play a key role in segmenting UAE audiences effectively, offering a balance of precision and adaptability as data volumes grow.
Computational Efficiency
Random forests strike a great balance between delivering reliable results and keeping computational demands in check. Unlike deep learning models, which often require significant computing power, random forests work efficiently with structured data. This makes them a smart choice for analysing complex customer behaviours without compromising on quality or overloading resources.
6. Neural Networks
Neural networks take audience segmentation to a new level by identifying patterns that traditional clustering and decision tree methods might miss. Unlike older approaches that rely on static demographic filters, these advanced models adapt dynamically to incoming data. They refine audience segments in real time based on digital interactions and transaction patterns. What makes them stand out is their ability to handle high-dimensional data - think dozens or even hundreds of variables - while preserving the relationships between them, thanks to dimensionality reduction techniques.
Handling Noisy or Complex Data
Neural networks are particularly effective when working with messy or incomplete datasets. For example, Self-Organising Maps (SOM) can train themselves while ignoring incomplete data points during weight adjustments, making them resilient to missing values. Additionally, customised neural embeddings can transform complex variables - like "shifting tastes" or "viewing velocity" - into mathematical vectors, enabling more precise clustering. This flexibility allows businesses to process and analyse vast, intricate datasets with ease.
Scaling for Large Datasets
When it comes to scalability, neural networks can handle millions of data points, provided batch processing is used. Without optimised code, embedding processes may fail with large datasets. Batch processing divides these datasets into smaller, manageable chunks, ensuring smooth encoding and computational efficiency. This method is particularly useful when utilising transformer-based models like SentenceTransformers for text-based segmentation. For businesses in the UAE's fast-paced digital market, this scalability makes neural networks an excellent choice for analysing customer bases ranging from thousands to millions.
Decoding the "Black Box"
One of the main criticisms of neural networks is their "black box" reputation, where results can be challenging to interpret. As Karyna Naminas, CEO of Label Your Data, points out:
"The black-box nature of deep learning models can make the results hard to interpret. You have to be careful to avoid biases in the training data, as this can lead to inaccurate segmentation".
To address this issue, businesses can use Large Language Model prompts to better understand cluster profiles and convert complex outputs into actionable strategies. Tools like U-matrices also help by visualising neuron distances, making it easier to spot distinct clusters and outliers in noisy data. At Wick, we've found that combining neural networks with more transparent models strikes a balance between depth and clarity, offering both powerful insights and understandable results.
Managing Computational Demands
Training neural networks can be resource-intensive, requiring significant computational power. However, transformer-based models are efficient at processing text data for segmentation tasks. By optimising hyperparameters such as learning rates and batch sizes, businesses can manage costs without compromising accuracy. For organisations without advanced computing infrastructure, cloud platforms offer a practical solution. These platforms scale resources based on demand, making neural networks accessible even for mid-sized businesses in the UAE market.
7. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
Principal Component Analysis (PCA) is not a clustering method in itself but a powerful dimensionality reduction tool. It simplifies high-dimensional datasets by transforming them into a smaller set of principal components that capture the most variance in the data. This process not only reduces complexity but also improves the speed and accuracy of audience segmentation, making it a valuable preparatory step for clustering algorithms.
Handling Noisy or Complex Data
One of PCA's strengths is its ability to manage noisy and complex datasets. It achieves this by converting highly correlated features - like "total purchase amount" and "average purchase amount" - into uncorrelated components. For instance, when features have correlation coefficients above 0.8, PCA ensures they don't skew clustering results by eliminating overlapping influences. This feature is particularly useful in the UAE's e-commerce landscape, where data often comes from diverse sources like CRM systems, transaction logs, and web analytics. To identify which features would benefit from PCA, you can start by computing a correlation matrix.
Scalability for Large Datasets
PCA is well-suited for large datasets, offering both scalability and efficiency. It has been deployed successfully on datasets with over 1,000,000 sessions using cloud-based tools like Google Colab. For example, in March 2023, Foursquare used PCA to reduce 16 features from a dataset of 100,000 users into just 10 principal components, preserving 80% of the variance. This allowed for precise K-means clustering. In another case, 14 principal components managed to retain at least 90% of the total information from a complex customer dataset. These examples highlight how PCA supports clustering models like K-means by simplifying data without losing critical insights.
Balancing Interpretability
One drawback of PCA is that it reduces direct interpretability. Since principal components are linear combinations of the original variables, it can be harder to pinpoint which specific features - such as age or income - are driving a particular segment. Foursquare acknowledges this trade-off:
"Despite the loss of some interpretability that occurs when dimensionality reduction is performed using PCA, the benefits of utilising lower dimensional data in the K-means clustering algorithm remain".
To maintain clarity, it's essential to document the combined features and use tools like a cumulative explained variance (Scree) plot to determine how many components to retain.
Improving Computational Efficiency
By reducing the number of features, PCA enhances the computational efficiency of clustering algorithms. Preprocessing steps, such as standardising data with tools like StandardScaler, ensure that algorithms perform effectively. This streamlined approach is particularly valuable for businesses in the UAE, where customer datasets can range from thousands to millions. By simplifying data, PCA lays the groundwork for effective clustering, as discussed in earlier sections.
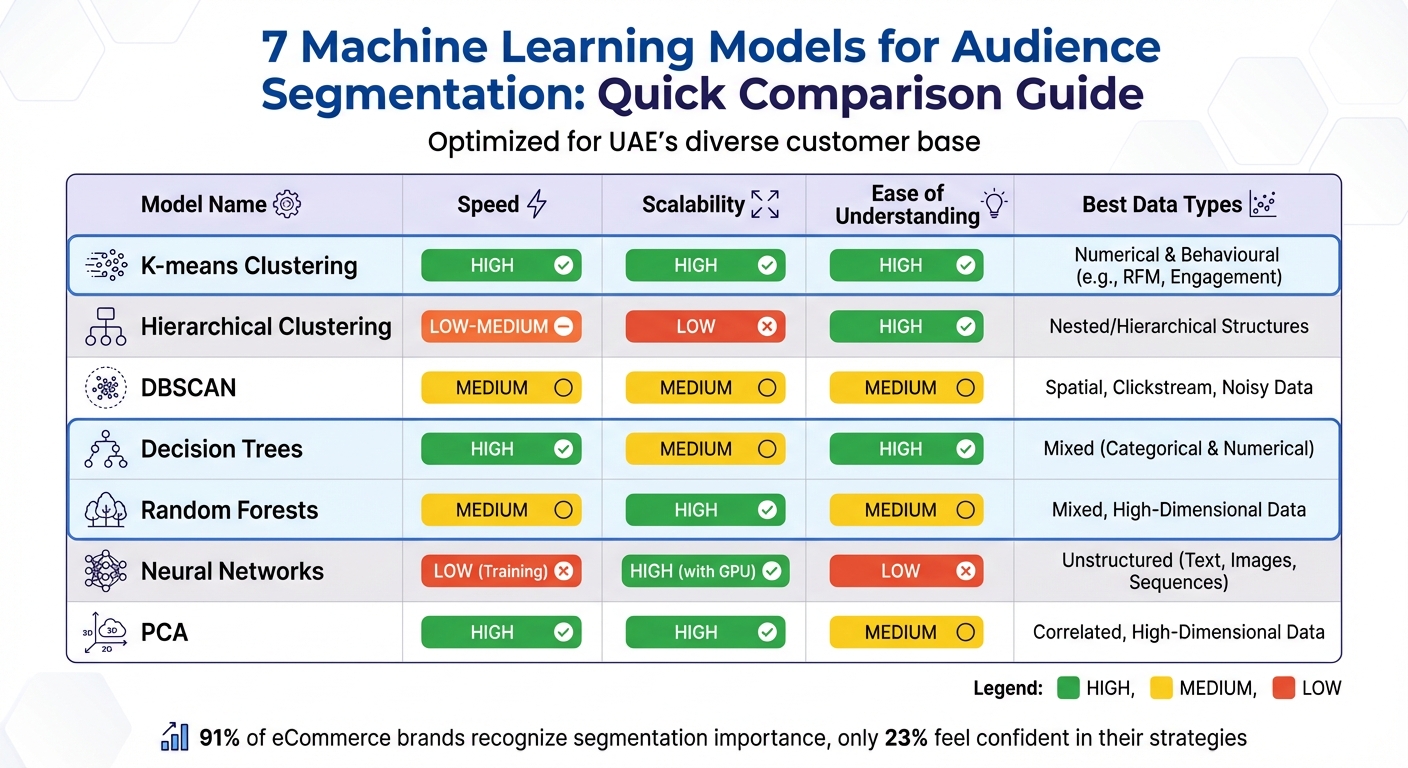
Model Comparison Table
Machine learning (ML) models offer a range of options for dynamic audience segmentation in the UAE, each with its own strengths. The best choice depends on your business goals, the type of data you’re working with, and the resources you have available.
Here’s a quick comparison of key performance factors across popular ML models:
| Model | Speed | Scalability | Ease of Understanding | Best Data Types |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| K-means | High | High | High | Numerical & Behavioural (e.g., RFM, Engagement) |
| Hierarchical | Low to Medium | Low | High | Nested/Hierarchical Structures |
| DBSCAN | Medium | Medium | Medium | Spatial, Clickstream, Noisy Data |
| Decision Trees | High | Medium | High | Mixed (Categorical & Numerical) |
| Random Forests | Medium | High | Medium | Mixed, High-Dimensional Data |
| Neural Networks | Low (Training) | High (with GPU) | Low | Unstructured (Text, Images, Sequences) |
| PCA | High | High | Medium | Correlated, High-Dimensional Data |
This table serves as a guide to help you align your model selection with specific segmentation needs.
For businesses aiming to maximise marketing ROI - potentially increasing returns by 5–10× - it’s important to weigh your computing resources. If processing power is limited, clustering methods like K-means or Decision Trees are practical choices. On the other hand, industries requiring high precision, such as healthcare or autonomous systems, may find the computational demands of Neural Networks worthwhile.
"Machine learning-based segmentation methods, particularly clustering algorithms like K-means and dimensionality reduction techniques such as Principal Component Analysis (PCA), tend to deliver robust results for a broad range of use cases".
This insight comes from Arjun Bali, Senior Data Scientist at Rocket Mortgage, highlighting the reliability of these approaches in diverse applications.
Conclusion
Choosing the right model boils down to your goals, the nature of your data, and the resources at hand: K-means is great for grouping numeric data, decision trees provide straightforward rules, neural networks uncover intricate patterns, and DBSCAN shines when dealing with noisy datasets.
In the UAE, customer segmentation comes with its own set of challenges. The region's diverse, multilingual population and the demand for real-time behavioural insights make the task even more complex. While 91% of eCommerce brands acknowledge the importance of segmentation for personalisation, only 23% feel confident in their current strategies. This gap highlights why expert support often becomes essential.
"Purchase behaviour is the clearest predictor of purchase intent. Most brands sit on this data, but few operationalise it effectively."
– Sumeet Bose, Content Marketing Manager, Saras Analytics
To implement effective segmentation, you need solid groundwork: proper data preparation, validation techniques (like the Elbow Method or Silhouette Scores), and ongoing refinement to keep up with evolving consumer behaviour. Brands leveraging AI for advanced segmentation have reported 5–10× higher marketing ROI compared to those sticking to static approaches.
For businesses in the UAE, partnering with a data-focused consultancy like Wick can make all the difference. They help fast-track implementation, ensure compliance with local regulations, and address the unique challenges of the market. With the right expertise, you can turn technical know-how into real-world business success.
FAQs
What should I consider when selecting a machine learning model for audience segmentation?
When selecting a machine learning model for audience segmentation, it's essential to match the model's strengths with your data and business goals. For instance, if you're working with large datasets that feature intricate patterns - like detailed customer interactions or purchasing habits - advanced models such as deep learning or gradient-boosted trees can uncover insights that might otherwise go unnoticed. On the other hand, if you need real-time updates, models that support incremental learning or online clustering are a better fit.
The type of data you're working with is another critical factor. For categorical data like age, gender, or location, decision trees are a practical choice. However, for continuous variables such as average spending or session duration, clustering techniques or neural networks tend to perform better. Also, think about how easily you can explain the model's outcomes to others. Simpler models like k-means clustering or decision trees are much easier to present to stakeholders compared to more complex options like neural networks.
Finally, weigh the computational demands and the potential return on investment. While complex models might offer greater accuracy, they also require more processing power and specialised expertise. Wick’s deep understanding of data-driven marketing supports businesses in the UAE by helping them choose models that align with their needs. They offer customised solutions, including AI-driven personalisation, data analytics, and marketing automation, tailored to the unique demands of the local market.
How can businesses in the UAE use machine learning to improve audience segmentation?
Businesses in the UAE can use machine learning (ML) to craft dynamic audience segments based on behaviours, preferences, and predicted value, moving beyond traditional static demographics. This approach is particularly impactful in a diverse market like the UAE, where consumers frequently switch between platforms in languages like Arabic, English, and Hindi, and where events such as Ramadan heavily influence shopping patterns.
To make the most of ML, companies should focus on three key steps:
- Prepare your data: Gather and clean data from sources like CRM systems, website analytics, and social media. Enhance this data with localised insights, such as nationality, preferred language, and transaction values in د.إ (AED). This ensures the data reflects the UAE's unique consumer landscape.
- Choose and train the right models: Start with unsupervised models, like clustering, to identify natural audience groupings. Then, use supervised models, such as decision trees, to predict important behaviours like customer retention or repeat purchases.
- Activate and measure outcomes: Put these audience segments to work across marketing channels, including email, SMS, and programmatic ads. Track success using metrics like revenue and conversion rates, ensuring all values are measured in د.إ and follow UAE-standard formats (e.g., 1,250.75 د.إ).
For businesses looking to simplify this process, partnering with Wick can be a game-changer. Wick’s Four-Pillar Framework combines AI-driven personalisation, data analytics, and marketing automation to design strategies that align with UAE cultural nuances while delivering measurable results.
Why are neural networks considered highly effective for audience segmentation?
Neural networks stand out when it comes to audience segmentation, thanks to their ability to handle complex, high-dimensional data like user behaviours and preferences with impressive precision. They can uncover subtle patterns and connections that simpler models might overlook, giving marketers a deeper understanding of their audience.
What’s more, neural networks are dynamic and flexible, allowing them to respond to shifts in audience behaviour as they happen. This capability makes them a powerful tool for crafting personalised, real-time marketing strategies that cater to the unique needs of different audience segments.
