Blog / Top AI Ethics Guidelines for Marketers
Top AI Ethics Guidelines for Marketers
AI has reshaped marketing, but its rapid adoption brings ethical challenges. To maintain trust, marketers must prioritize transparency, human oversight, and data privacy. Here’s what you need to know:
- Disclose AI Use: Be upfront about AI involvement in content creation. Add disclaimers and use platform tools like Meta’s AI tags or TikTok’s AI switch.
- Human Review: Always verify AI-generated content for errors, biases, and copyright issues.
- Data Governance: Categorize data by risk, avoid sensitive information, and ensure compliance with privacy laws like UAE’s Federal Decree Law No. 45 of 2021.
- Consent-Driven Data Use: Obtain explicit user consent for personal data use and offer clear opt-in/opt-out options.
- Quality over Quantity: Focus on accurate, well-crafted content rather than bulk AI outputs.
- Document Policies: Define clear AI usage guidelines, including acceptable tools and prohibited data types.
- Maintain Human Connections: Use AI as a tool, not a replacement, to preserve your brand’s voice and emotional depth.
Ethical AI practices aren’t just about compliance - they build trust and protect your brand. With regulations like the EU AI Act and UAE laws evolving, staying responsible is key to long-term success.
1. Disclose When You Use AI in Content
Why Transparency in AI Content Matters
Consumers are increasingly wary of undisclosed AI-generated content. A staggering 94% of people believe brands should disclose when AI is involved in creating content. Yet, audiences only correctly identify AI-generated text 57.3% of the time and AI-generated images 53.4% of the time. Adding to this, around 41–42% of consumers express discomfort when brands use AI for tasks like writing product descriptions or taglines. Transparency is key. As Naomi Bleackley, Editorial Account Manager and AI specialist at VeraContent, puts it:
"AI is not human - it doesn't think, work or understand as we do".
These concerns have led to the development of stricter regulations to address this growing challenge.
Staying in Line with Regulations and Industry Guidelines
On 15 January 2026, the Interactive Advertising Bureau (IAB) introduced the AI Transparency and Disclosure Framework. This framework takes a risk-based approach, requiring disclosure only when AI use significantly impacts authenticity, identity, or representation in ways that could mislead consumers. Routine tasks or clearly stylised creative content are exempt from this requirement. Similarly, the EU AI Act's Article 50, which will be fully enforced by August 2026, focuses on ensuring manipulated content like deepfakes is easily identifiable. As the European Commission explains:
"The obligations under Article 50 of the AI Act... aim to ensure transparency of AI-generated or manipulated content, such as deep fakes. The article addresses risks of deception and manipulation, fostering the integrity of the information ecosystem".
With these frameworks in place, businesses must adopt practical strategies to ensure compliance and maintain trust.
Practical Steps for Disclosure
To uphold transparency, start by revising client agreements. Include clauses in your Master Service Agreements that outline AI's role in delivering services and clarify liability. For AI-generated images, credit the specific AI model in the photo caption. When publishing written content, add disclaimers like: "This article was created with some help from AI, but edited, reviewed, and fact-checked by a real person".
Leverage platform-specific tools to help with disclosure. For example:
- Use Meta’s AI info tag.
- Enable YouTube’s studio checkbox for AI content.
- Activate TikTok’s AI switch.
- Clearly label AI-generated images with a visible "Created using AI" tag.
If deepfake content is used for humour or illustrative purposes, explicitly state this to avoid misleading your audience.
Building Trust Through Transparency
Being upfront about AI use isn’t just about following regulations - it’s about earning consumer trust. J.R. Tulloch, Attorney at Fourscore Business Law, highlights this point:
"Transparency is not just an ethical best practice - it is increasingly becoming a legal and regulatory necessity".
In regions like the UK, the ISBA and IPA have issued guidelines stressing the importance of disclosure when AI involvement isn’t immediately clear. Similarly, in the UAE, where high social standards are valued, openly acknowledging AI involvement strengthens consumer confidence.
Remember, the level of disclosure required depends on the context. For example:
- AI chatbots must inform users they are interacting with a bot.
- Deepfakes should be clearly labelled as "Artificially Generated" or "Manipulated."
- AI-generated news or articles should include disclaimers for both editors and readers.
However, for internal research summaries reviewed by a human before client delivery, disclosure is generally not necessary.
2. Require Human Review for All AI Content
Tackling Ethical Concerns in AI Content Marketing
AI may churn out content at lightning speed, but it lacks the ability to grasp subtle errors or context. Without proper oversight, AI-generated content can lead to inaccuracies, intellectual property issues, or even perpetuate harmful stereotypes. In fact, over half of major brands express serious concerns about the risks associated with generative AI, including intellectual property violations, copyright breaches, privacy concerns, and brand safety issues. The UAE Charter for the Development and Use of Artificial Intelligence, introduced on 10 June 2024, highlights "Human Oversight" as a core principle. It underscores that human judgement is indispensable for identifying and correcting errors or biases, especially in a market as discerning as the UAE's.
Practical Steps for Implementation
To ensure quality and accuracy, it's crucial to establish a robust fact-checking process. Assign reviewers to scrutinise AI-generated content for biases and verify originality. For instance, if you're using AI to gauge social sentiment, cross-check the results against a random sample of the underlying data to confirm reliability. This proactive approach to fact-checking not only mitigates risks but also aligns with emerging regulatory expectations.
Staying in Line with Industry Regulations
Regulations worldwide are increasingly demanding human oversight for AI-generated content. The EU AI Act, set to be fully enforced by August 2026, explicitly differentiates between fully automated content and content reviewed by humans. According to Article 50, AI-generated materials that have undergone human review - especially those addressing public interest - might even be exempt from some labelling requirements, provided they meet editorial standards.
Building Trust and Protecting Reputation
Human oversight isn’t just about compliance - it’s about safeguarding your brand’s reputation. With three out of four of the world’s largest brands already incorporating or planning to incorporate generative AI into their marketing strategies, maintaining rigorous quality control is non-negotiable. Gabrielle Robitaille, Policy Director at the World Federation of Advertisers, highlights this point:
"Mitigating these risks might involve... ensuring human review of outputs to identify whether any assets resemble existing copyright or IP-protected works and whether they contain personal data".
In a region like the UAE, where ethical standards and social values hold significant weight, demonstrating a commitment to responsible AI practices through consistent human oversight not only ensures compliance but also reinforces consumer trust in your brand.
3. Create Clear Data Governance Rules
Tackling Ethical Challenges in AI Content Marketing
Using data within AI tools comes with serious ethical and legal risks. Without clear governance, marketers risk misusing data that may have been collected unethically or violating privacy laws. This can lead to significant legal trouble and reputational harm. While AI systems thrive on data, not all data is fair game - and distinguishing between what’s appropriate and what’s not requires a structured approach.
Data governance isn’t just about what’s possible with AI; it’s about what’s responsible. Gabrielle Robitaille, Policy Director at the World Federation of Advertisers, highlights this responsibility:
"Our challenge is to make sure it's used for good. There are opportunities for brands as well as novel challenges. None of these are insurmountable, but they do require CMOs to take active steps to mitigate the legal, ethical and reputational risks".
By building on ethical practices, clear governance ensures that every decision involving AI respects data integrity and aligns with values.
Practical Steps for Implementation
The first step is to categorise your data based on risk levels and document all data sources. High-risk data - such as Protected Health Information, student records, social security numbers, or home addresses - should never be used in AI prompts or uploaded to generative tools. Create a list of prohibited data types and ensure your team is well-informed about these boundaries. For data classified as moderate risk, set up approval processes before any use.
When acquiring AI tools, carefully examine the vendor's Terms of Use. Some providers might reserve the right to use your brand name or proprietary data in their marketing efforts, which could conflict with your company’s policies.
For tasks involving heavy data use, like monitoring social media sentiment, always verify AI-generated summaries against raw data samples to ensure accuracy and reliability.
Staying in Line with Regulations and Industry Standards
Under frameworks like the UK GDPR, it’s essential to have a lawful basis - such as consent, contract, or legitimate interest - before processing personal data for AI purposes. The Information Commissioner’s Office advises:
"The development and deployment of AI systems involve processing personal data in different ways for different purposes. You must break down and separate each distinct processing operation".
This means treating each stage - whether it’s training models or deploying them - as separate processes, each requiring its own legal justification.
For high-risk processing activities, conduct Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs) to evaluate how your AI systems might affect individuals’ rights and freedoms. The UK's Data (Use and Access) Act, introduced in June 2025, underscores fairness and transparency as key principles - offering a regulatory framework that supports innovation while protecting consumers.
Strengthening Brand Reputation Through Responsible Practices
Clear data governance isn’t just about avoiding breaches - it’s about building trust. In the UAE, where ethical standards and values hold significant importance, responsible data practices are crucial for maintaining consumer confidence. By demonstrating that you’ve restricted high-risk data, documented sources, and maintained human oversight, you’re not just meeting legal requirements - you’re positioning your brand as one that genuinely respects its customers.
With three out of four of the world’s largest brands already leveraging generative AI in marketing, the competitive landscape is evolving quickly. The brands that succeed will be those that establish strong governance frameworks now, ensuring they avoid the reputational fallout of a data breach or ethical misstep.
4. Document Your AI Strategy and Policies
Tackling an Ethical Challenge in AI Content Marketing
Without clear policies, AI use can become inconsistent, exposing organisations to accountability gaps and legal risks. Employees lacking proper guidance might misuse sensitive data, infringe on intellectual property rights, or produce misleading content. Documented policies turn vague intentions into enforceable standards, safeguarding both your brand and your customers. Similar to guidelines on data governance and human oversight, formal AI policies ensure secure and consistent practices.
A great example comes from Stanford University, which launched the "Stanford AI Playground" in January 2025. This secure platform allowed staff to experiment with large language models while ensuring uploaded files were neither shared externally nor used for model training. By clearly documenting policies, organisations can build on existing practices of data governance and transparency, creating a more secure environment for AI use.
Steps to Implement AI Policies
Start by defining what "AI" and "generative AI" mean for your organisation. Be specific about which tools are included and who the policy applies to - employees, consultants, interns, or others. Establish core ethical principles, such as treating AI outputs with the same responsibility you’d expect from others.
Set clear disclosure guidelines to ensure transparency when AI significantly impacts the authenticity of content. Require human oversight to check AI outputs for accuracy and ethical compliance. Additionally, outline acceptable AI use cases for tasks like social media monitoring, image editing, and drafting press releases. Explicitly state which types of data are prohibited from being used as AI prompts, ensuring sensitive information remains protected.
Aligning with Industry Standards and Regulations
Your AI documentation should include transparency mechanisms that align with industry standards. For example, the Coalition for Content Provenance and Authenticity (C2PA) offers a framework for tracking digital content history through metadata. Combining visible labelling with invisible watermarking ensures content remains identifiable, even after edits. This supports consumer rights and prepares for evolving regulatory requirements.
Maintain an audit trail of data sources and the legal status of all AI inputs. As regulations like the EU AI Act and other international frameworks develop, this documentation becomes essential. Regularly assess your AI tools to confirm they meet both institutional expectations and updated regulatory standards.
Building Brand Trust and Reputation
Transparent policies can set your brand apart. The National Artificial Intelligence Centre highlights this point:
"Being transparent about your use of AI‑generated content may help to create a point of difference with your competitors. It can also support your business to build a foundation of trust with your consumers".
In the UAE, where ethical standards are highly valued, transparency shows respect for your audience’s right to know how content is created. Clear documentation also shields your brand from reputational harm caused by fraud, misinformation, or malicious activities. By making AI-generated content easily identifiable, you can mitigate risks. With fewer than 1% of enterprises effectively using AI agents, those that establish strong governance frameworks can position themselves as industry leaders. This approach not only builds trust but also complements broader commitments to ethical AI practices.
5. Focus on Content Quality, Not Volume
Tackling Ethical Challenges in AI Content Marketing
The rise of AI tools has made generating content faster and easier than ever, but this convenience can lead to a dangerous trade-off: speed over quality. A staggering 75% of the world's largest brands are either already leveraging generative AI in their marketing or plan to do so soon. Yet, over half of these brands express deep concerns about the risks, particularly in areas like reliability, safety, and integrity. Without proper oversight, AI-generated content can slip through with inaccuracies, harmful stereotypes, or even copyright violations. Such missteps don't just hurt campaigns - they erode brand credibility.
This is where marketers play a crucial role. The need for human oversight isn’t just a good practice; it’s an ethical responsibility.
Practical Steps to Ensure Quality
To avoid falling into the trap of unchecked AI outputs, implement a robust human review system. Make it standard practice to fact-check and scan all AI-generated content for plagiarism before it goes live. For social media monitoring, cross-verify AI outputs with source data to spot potential errors.
Set clear quality benchmarks that emphasise professional standards and thoughtful analysis over sheer output speed. AI can be a fantastic tool for brainstorming and editing, but the final review should always remain in human hands. As Stanford University highlights, AI is most effective when it augments human work rather than replacing it.
Strengthening Brand Trust and Reputation
By prioritising quality over quantity, your organisation can position itself as a trusted and responsible leader in the industry. In the UAE, where ethical practices and consumer trust hold particular importance, delivering high-quality, human-reviewed content helps build meaningful, long-term relationships. Simply churning out content won’t achieve that - earning trust requires consistent attention to detail and integrity.
sbb-itb-058f46d
6. Get Permission Before Using Personal Data
Tackling an Ethical Challenge in AI Content Marketing
When it comes to ethical AI use, obtaining clear consent isn't just a legal requirement - it’s a cornerstone of responsible data practices. AI marketing tools are capable of processing massive amounts of personal data to create tailored campaigns, predict customer behaviour, and personalise content. But using personal data without explicit permission not only violates ethical principles but also exposes your organisation to serious legal consequences. The Information Commissioner's Office (ICO) emphasises this point:
"Consent means offering individuals real choice and control. Genuine consent should put individuals in charge, build trust and engagement, and enhance your reputation".
In the UAE, Federal Decree Law No. 45 of 2021, effective from 2nd January 2022, makes it clear: personal data cannot be processed without the owner’s consent, except under specific legal exceptions. This law also regulates "Profiling", which involves automated processing to assess preferences, behaviours, and locations - a core feature of AI-driven marketing. Additionally, using someone’s likeness in AI-generated content without explicit permission may lead to significant financial liabilities.
Steps to Implement Ethical Consent Practices
To comply with UAE law and ethical standards, implement a positive opt-in system. Avoid pre-checked boxes or default consent settings. Instead, require clear affirmative actions such as ticking an empty box or clicking an "I agree" button. Ensure that consent options are specific, allowing users to agree to certain types of data usage while opting out of others. For instance, a user might approve personalised product recommendations but decline to have their data used for AI model training. The law mandates that consent be presented in a "clear, simple, unambiguous and easily accessible manner", so don’t bundle all permissions into a single "all-or-nothing" option.
Make it just as easy for users to withdraw consent as it is to give it. Include a "manage preferences" link on every page, accessible across devices. Record every instance of consent, noting the timing, method, and information provided. If you introduce new AI technologies or use existing data for different purposes, fresh consent must be obtained. The ICO suggests requesting updated consent for storage and access technologies every six months.
Meeting Regulatory and Industry Standards
These measures align with stringent regulations. Beyond UAE law, marketers should note that AI-driven insights into sensitive areas like health, religion, or political views may require explicit consent under "special category" data protections. If your AI system makes automated decisions - such as determining who receives premium offers - you must inform users about this.
For organisations handling large volumes of personal data or conducting systematic assessments, appointing a Data Protection Officer is essential. High-risk AI processing also calls for a Data Protection Impact Assessment to ensure transparency and accountability. Tools like the Digital Dubai AI Ethics Self-Assessment Tool can help evaluate whether your systems meet key standards for fairness, accountability, and transparency.
Building Trust and Protecting Your Reputation
Failing to secure valid consent can damage both compliance and trust. The ICO warns:
"This approach could destroy trust and harm your reputation – and may leave you open to large fines".
In the UAE, where ethical practices and consumer protection are highly valued, respecting data privacy isn’t just about following the rules - it’s a way to stand out in the market. Giving users genuine control over their data lays the groundwork for strong, lasting customer relationships. By being transparent about how your AI systems use personal data, you show respect for your audience and establish your brand as trustworthy and responsible in an increasingly privacy-conscious world.
7. Maintain Real Human Connections with Your Audience
Tackling an Ethical Dilemma in AI Content Marketing
While AI offers incredible efficiency, keeping genuine human connections at the centre of your content strategy is crucial. Relying solely on AI-generated content can erode trust in your brand. With AI already a staple for top companies, the real challenge is not adoption - it’s ensuring your authentic voice remains intact. As Paul Roetzer, Founder and CEO of Marketing AI Institute, aptly states:
"AI has the potential to make brands more human by enabling us to focus increased time and energy on communications, creativity, culture, community, and the human condition".
The ethical concern here is clear: AI can churn out content quickly, but it lacks the emotional depth, cultural subtleties, and personal experiences that make communication meaningful. Treating AI as a substitute rather than a tool risks creating content that feels impersonal. This can be particularly damaging in the UAE, where personal relationships and trust are at the heart of business and community.
Practical Steps to Keep the Human Touch
Start by refining your brand’s voice through precise prompt engineering. Instead of generic instructions like "write a social media post", provide detailed context and tone. For instance: "Create a warm, professional message tailored for small business owners in Dubai, focusing on inclusivity and encouragement". This ensures that AI-generated content reflects your unique identity rather than sounding generic.
Always include human oversight in the content process. Whether it's reviewing AI drafts or analysing social media trends, a human perspective is essential to ensure accuracy and alignment with your brand’s values. For example, when AI summarises audience sentiments, cross-check its findings against a sample of the actual data. While AI can spot patterns, only a human can interpret whether these patterns truly resonate with your audience’s emotions and expectations. By combining tailored AI inputs with thorough human review, you can create content that feels authentic and personal.
Strengthening Brand Trust and Reputation
By prioritising these practices, you lay the groundwork for authentic customer relationships. Over half of major brands express "extreme concern" about AI-related risks like intellectual property issues, privacy, and brand safety. Audiences today can sense when content lacks a human touch, and this perception can harm your credibility.
Use the time saved by AI to focus on creative storytelling and meaningful engagement. Let AI handle repetitive tasks like drafting or data analysis, but reserve the final touches - emotional depth, cultural relevance, and personal narratives - for your team. This approach aligns with Stanford’s "AI Golden Rule": use AI-generated content in ways you’d want others to use it with you. By blending AI efficiency with human creativity and oversight, you not only enhance content quality but also build trust and loyalty, reinforcing an ethical approach to AI in marketing.
What’s Real in AI Marketing? Ethics, Trust, and Transparency with Dr. Cecilia Dones
Comparison Table
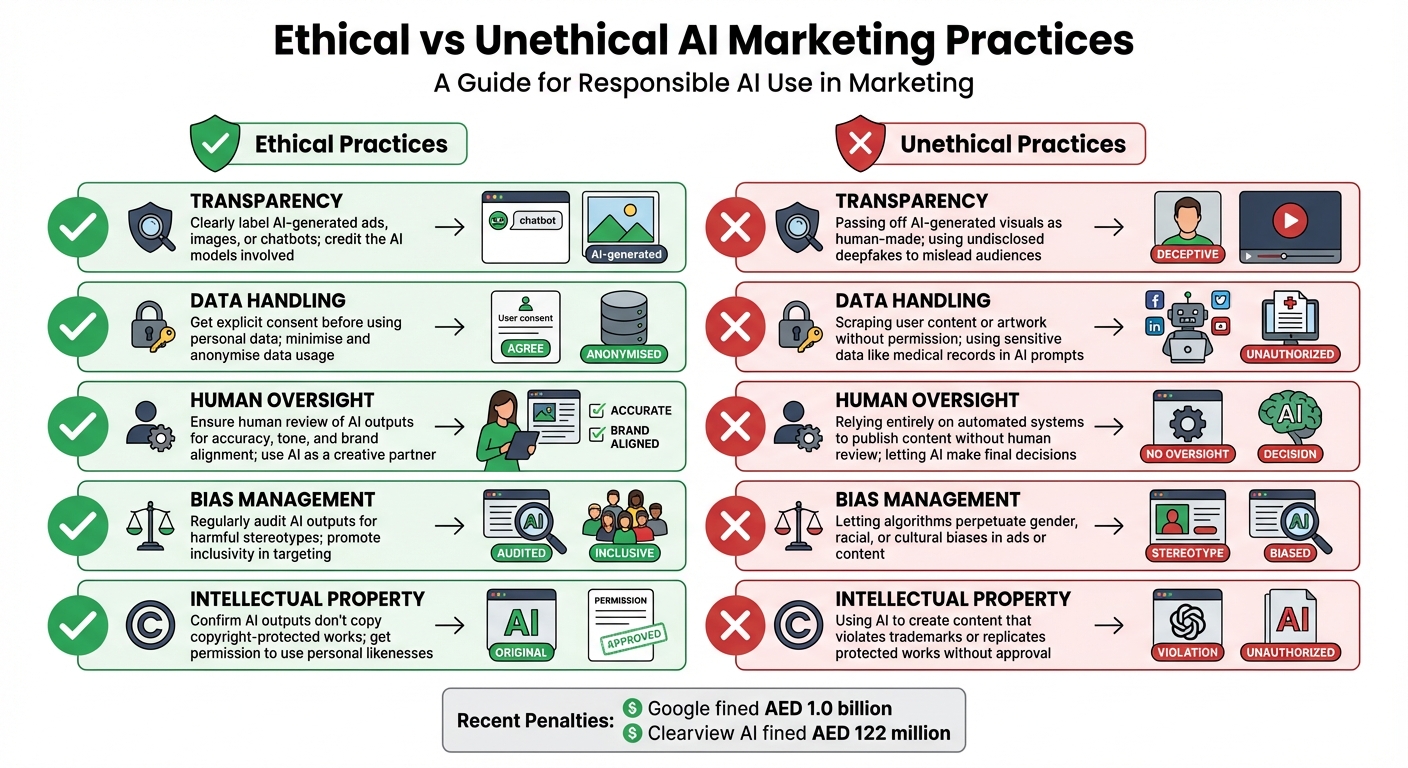
Ethical vs Unethical AI Marketing Practices for UAE Marketers
Understanding the difference between ethical and unethical AI practices is essential for maintaining trust and avoiding major risks. Below is a breakdown of key areas where marketers in the UAE need to make informed decisions about AI use in content creation.
| Practice Area | Ethical Approach | Unethical Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Transparency | Clearly label AI‐generated ads, images, or chatbots; credit the AI models involved. | Passing off AI‐generated visuals as human-made; using undisclosed deepfakes to mislead audiences. |
| Data Handling | Get explicit consent before using personal data; minimise and anonymise data usage. | Scraping user content or artwork without permission; using sensitive data like medical records in AI prompts. |
| Human Oversight | Ensure human review of AI outputs for accuracy, tone, and brand alignment; use AI as a creative partner. | Relying entirely on automated systems to publish content without human review; letting AI make final decisions. |
| Bias Management | Regularly audit AI outputs for harmful stereotypes; promote inclusivity in targeting. | Letting algorithms perpetuate gender, racial, or cultural biases in ads or content. |
| Intellectual Property | Confirm AI outputs don’t copy copyright-protected works; get permission to use personal likenesses. | Using AI to create content that violates trademarks or replicates protected works without approval. |
These distinctions show how ethical choices can directly influence compliance and reputation. Adhering to these principles not only helps avoid legal issues but also reinforces brand credibility. For instance, in March 2024, the French Competition Authority fined Google €250 million for training its Bard model on publisher content without proper notification. Similarly, in September 2024, Clearview AI faced a €30.5 million fine from the Dutch Data Protection Authority for violating GDPR with its facial-recognition database. These cases highlight the importance of ethical AI practices in avoiding legal penalties and safeguarding reputation.
For UAE marketers, following ethical AI practices ensures compliance with local regulations while fostering trust among consumers.
Conclusion
In today’s marketing landscape, ethical AI practices are no longer optional - they’re essential. The seven key principles - transparency, human oversight, data governance, documented policies, focus on quality, consent-driven data use, and genuine human connections - serve as the backbone for earning and maintaining consumer trust in the UAE. These principles not only build trust but also shield brands from costly penalties.
Recent cases like Google’s AED 1.0 billion fine and Clearview AI’s AED 122 million penalty highlight how unethical AI practices can severely damage a brand’s reputation and finances. On the other hand, 50% of marketing leaders now acknowledge AI’s transformative role in boosting productivity. With AI becoming a cornerstone of modern marketing, adopting ethical practices isn’t just advisable - it’s essential.
"Ethical AI isn't just the right thing to do - it's a smart business move." - Digital Marketing Institute
For marketers in the UAE, aligning with ethical AI standards is critical for long-term success. These standards, tailored to UAE’s regulatory and cultural expectations, ensure compliance while fostering consumer loyalty. By leveraging AI to enhance human creativity, brands can maintain authentic connections and achieve sustainable growth. Trust, after all, is the currency of modern marketing.
FAQs
How can marketers make sure AI-generated content reflects their brand values?
To make sure AI-generated content truly represents your brand's values, start by laying out your core brand principles and weaving them into your AI usage policies. Use training data that reflects your brand's identity and tone, and always keep human oversight in place to review and approve the content AI generates. Set up a governance framework with regular audits, clear transparency practices, and employee training to ensure everything stays aligned and meets ethical standards.
How can marketers ensure compliance with data privacy laws when using AI in the UAE?
To align with the UAE's Personal Data Protection Law while integrating AI into marketing, it's essential to take specific steps to ensure compliance and protect user privacy:
- Audit your data: Review all personal data being used by your AI systems, including any information inferred from user behaviour. Make sure it complies with privacy regulations.
- Obtain proper consent: When necessary, get clear and informed consent from users. Ensure they can easily withdraw their consent if they choose.
- Minimise and anonymise data: Only collect and use data that is absolutely necessary for your objectives. Whenever possible, anonymise the data to lower the risk of breaches.
- Assess risks: For AI applications that involve higher privacy risks, conduct a Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIA). This helps identify and address potential issues before they arise.
- Secure your systems: Use strong encryption, limit access to sensitive data, and conduct regular security audits to keep personal data safe.
Being transparent is crucial - let users know how AI is being used, why it’s being used, and their rights to access, correct, or delete their information. By embedding these steps into your processes, you can integrate AI responsibly while adhering to the UAE’s privacy laws.
Why is human oversight important in AI-powered marketing strategies?
Human oversight is crucial for making sure AI-generated marketing content stays accurate, ethical, and in line with a brand's core values. By carefully reviewing AI outputs, marketers can catch and address issues like bias, mistakes, or unintended messaging that might damage a brand's reputation.
It also plays a key role in ensuring that content complies with regulatory standards and respects local sensitivities, especially in diverse markets such as the UAE. This careful attention helps maintain audience trust and upholds the credibility of your marketing campaigns.
